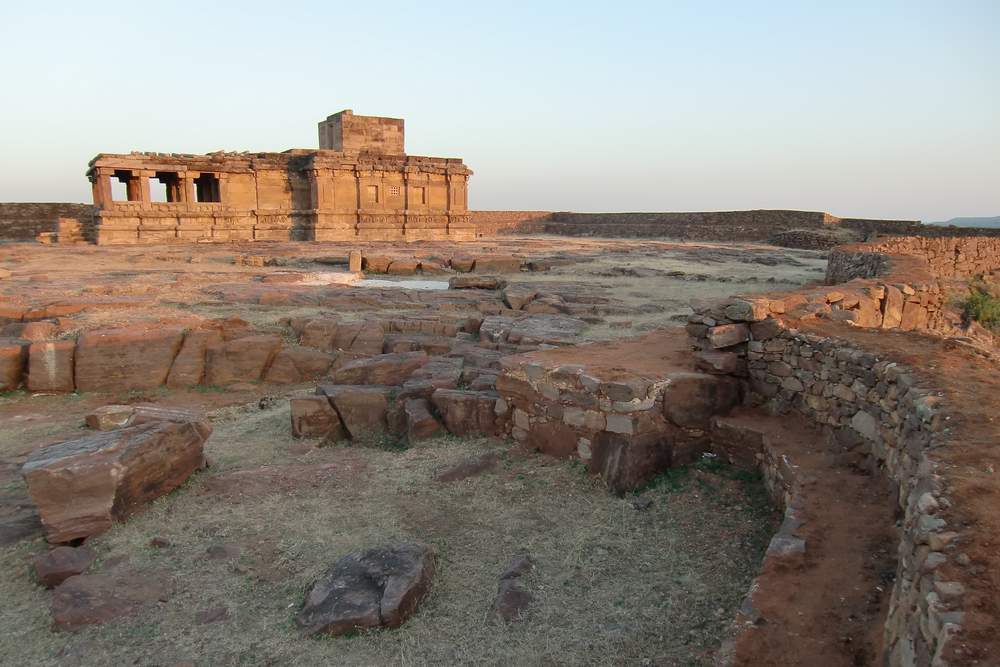

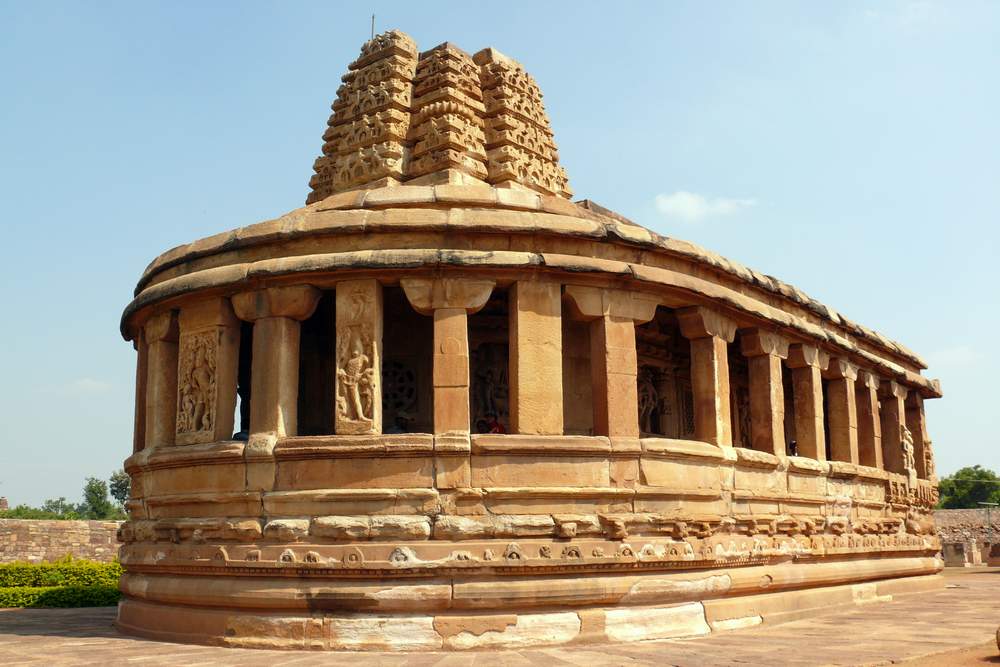
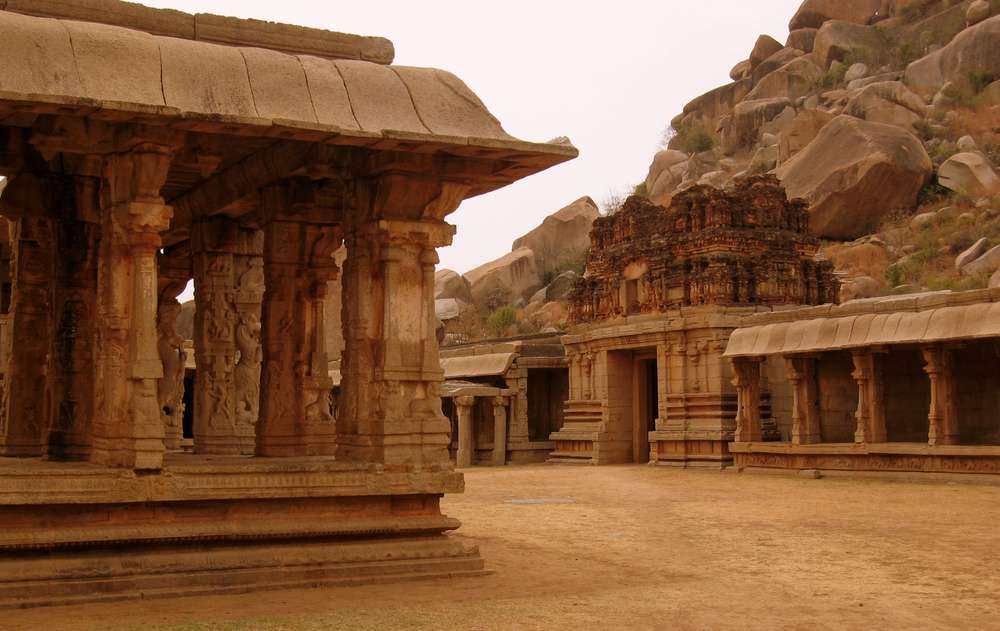
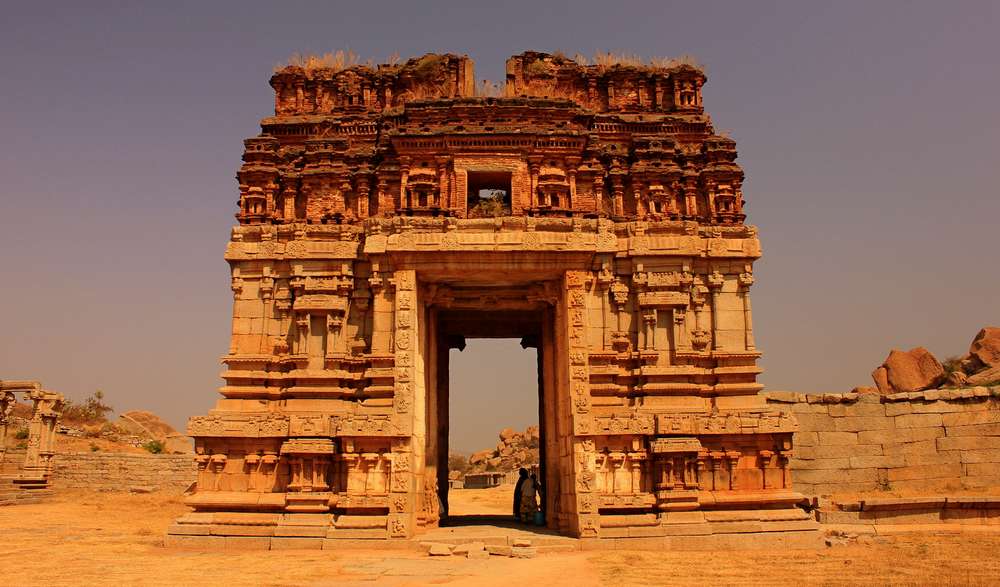
Aihole, ancient Ayyavole, now in Bijapur district was a great centre of early Chalukyan architecture. In fact this was the cradle of Chalukyan temples. Literally more than one hundred early-Chalukyan temples were built here in the sixth and seventh centuries CE.
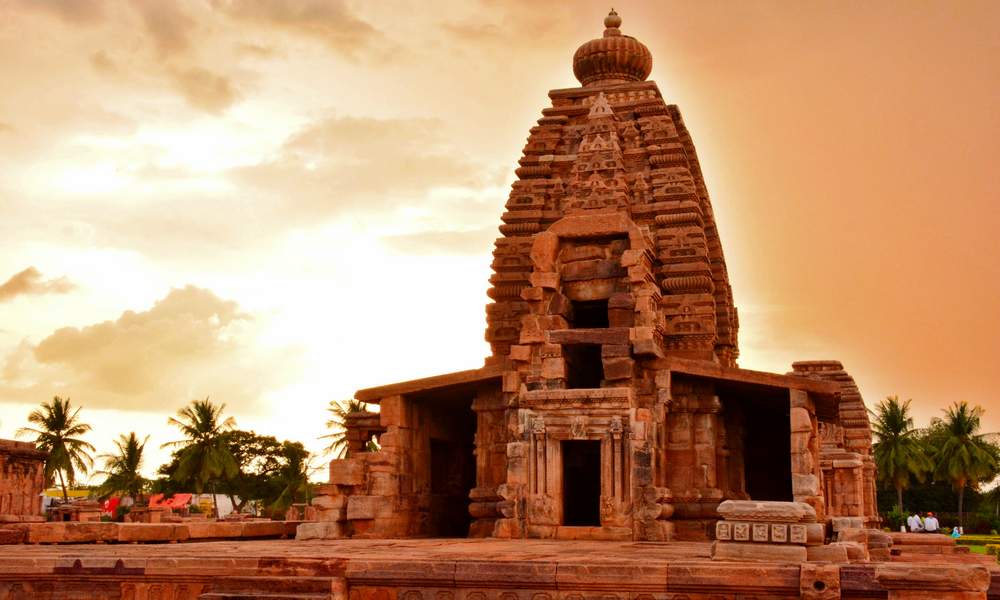
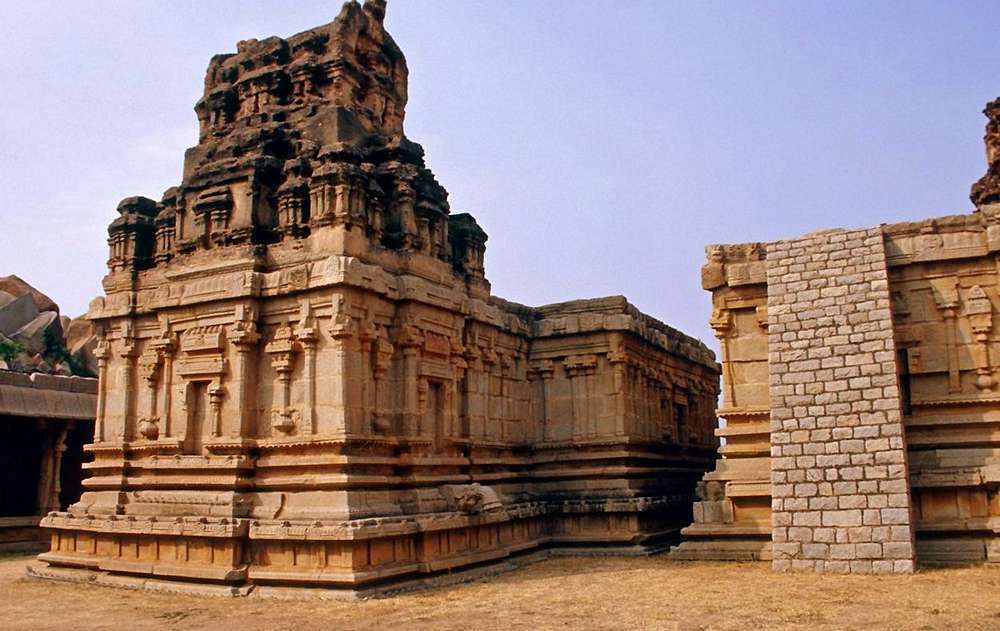
Meguti temple is one such temple at Aihole. This temple is built on a hillock and looks prominently even from a distance.
The Meguti Temple is also famous in Indian history and literature for the inscription written by the celebrated poet Ravikirti. This inscription mentions Kalidasa and Bharavi by name and for this reason highly useful for fixing the date of both these poets as the inscription is dated 634–35 CE. From this evidence, it becomes comprehensible that this temple was built in 634–35 CE. It also gives a graphic description of the eminent conquests of Chalukya Pulakesi II.
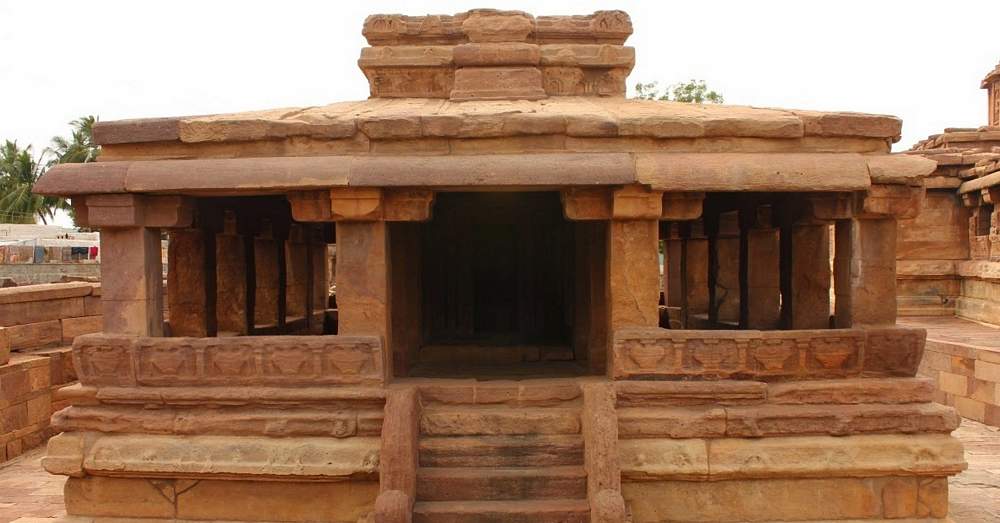
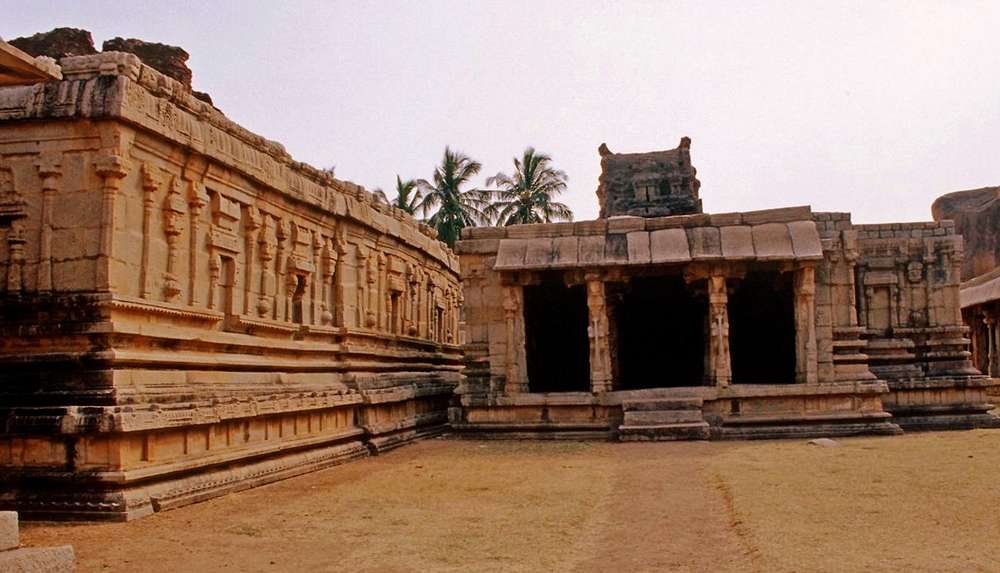
This is a Jain temple and stands on a basement of 4 ft and faces north. The temple consists of a garbhagriha, pradakshinapatha, antarala and a mandapa. The outer wall of the temple consists of two thick decorated moldings. The mandapa portion is open with square pillars above the moldings. Below the base moldings are carved chaitya type niches, amorous couples, musicians playing on musical instruments and wrestlers.
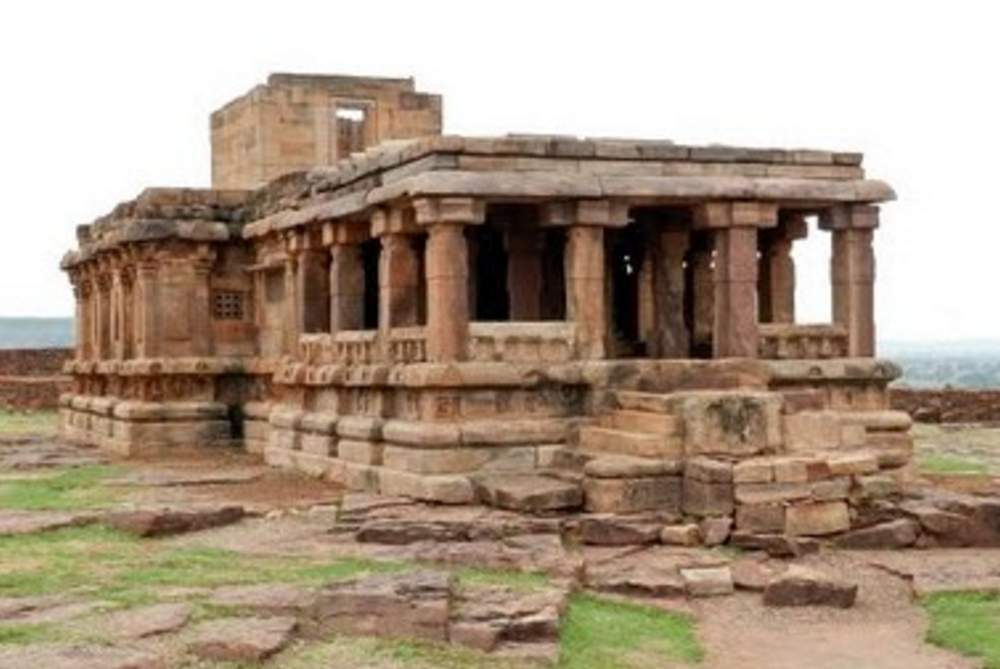

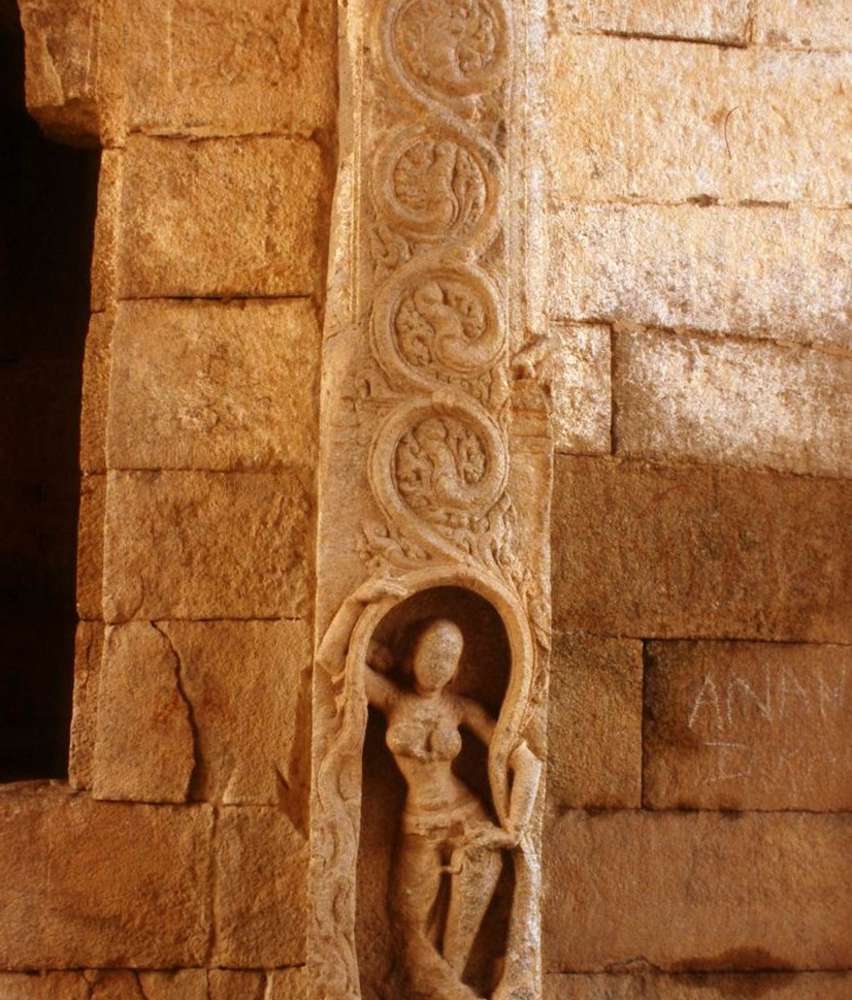
The square garbhagriha has a sitting tirthankara under a tree. Some scholars recognize him as Mahaveera. He is flanked by two chauri bearers on each side. Above the garbhagriha is another garbhagriha, which can be entered from the sukhanasi. In general, Jain temples (basadi) contain two garbhagrihas one over the other. On the western sidewall of this, is a very beautiful female sculpture which may be either Ambika or Siddhayika or Sujata. On her sides are chamara bearers and below are the sculptures of monkey and a swan. The upper garbhagriha has no sikhara over it. Its walls are also unadorned except niches, which are now empty.
Though this temple is not highly attractive from the point of view of the embellishments and decorations, it is notable in understanding the evolution of early Chalukyan art under the background that this is a dated temple assignable to 634–35 CE. This is the earliest dated temple of the Chalukyas of Badami.
This is one of the early temples where the Chalukyan architects were making experiments in the construction of a perfect temple. From the famous Ravikirti’s inscription this temple is better known than others.
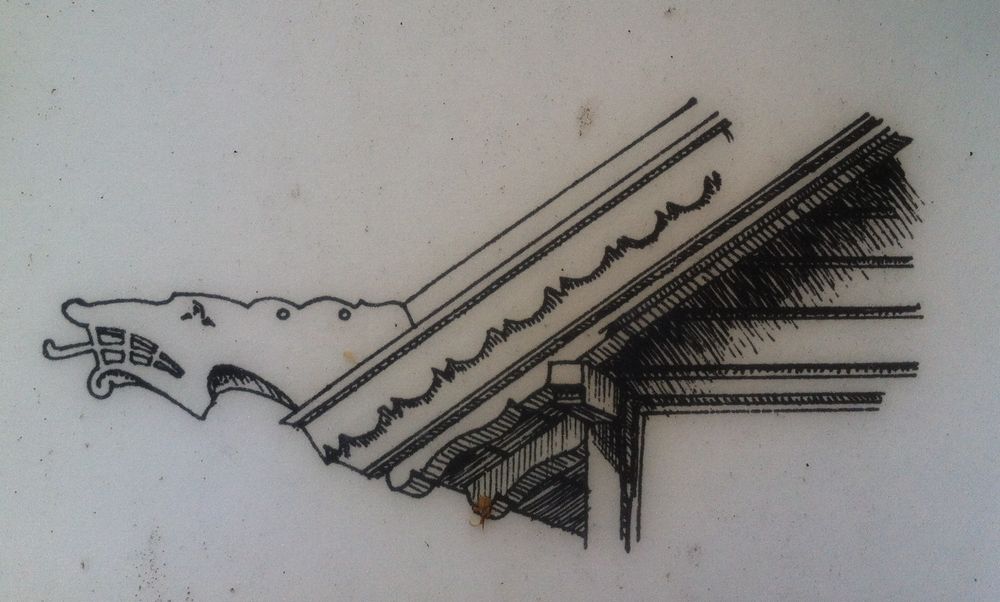
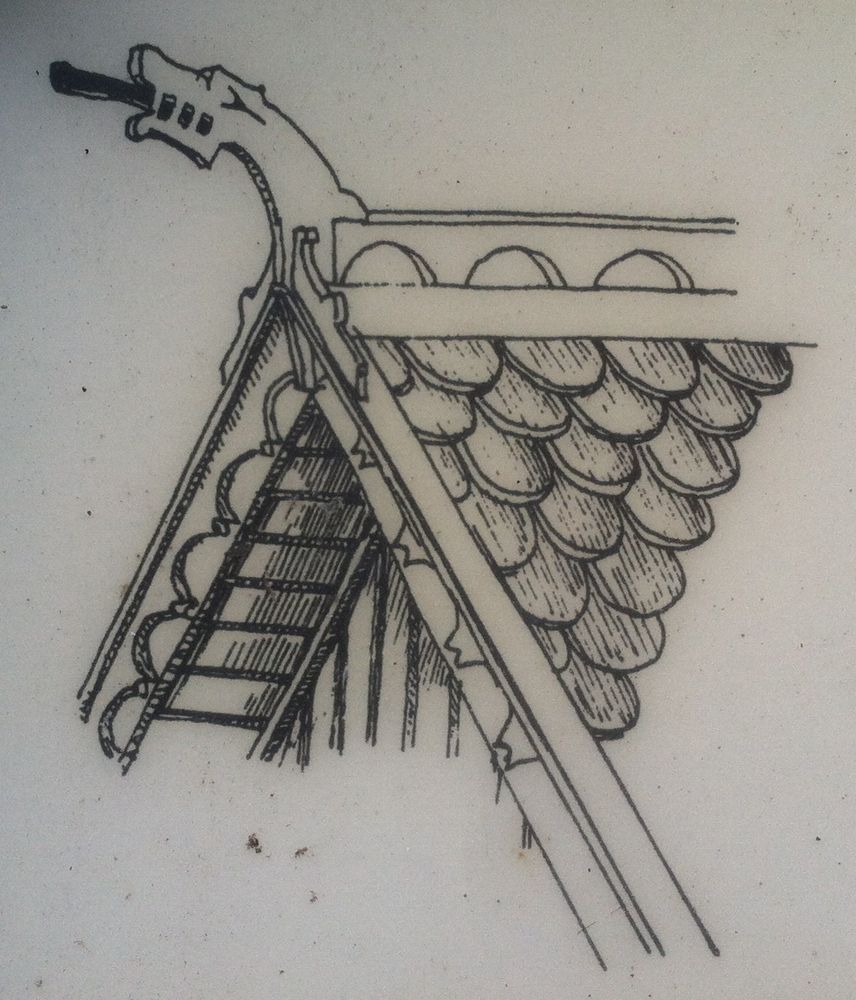










 The most important charm of this temple for which it is celebrated is the
The most important charm of this temple for which it is celebrated is the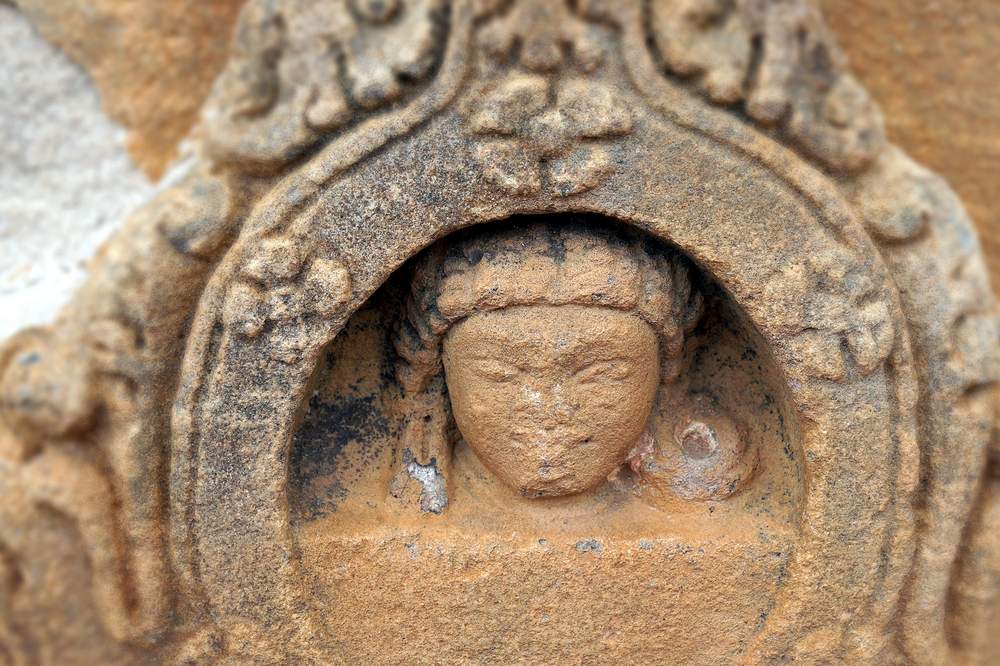 
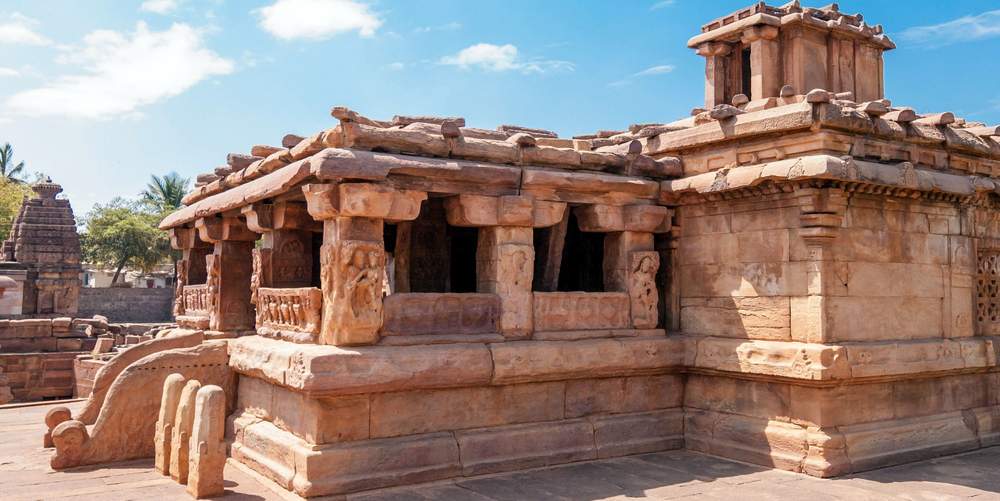
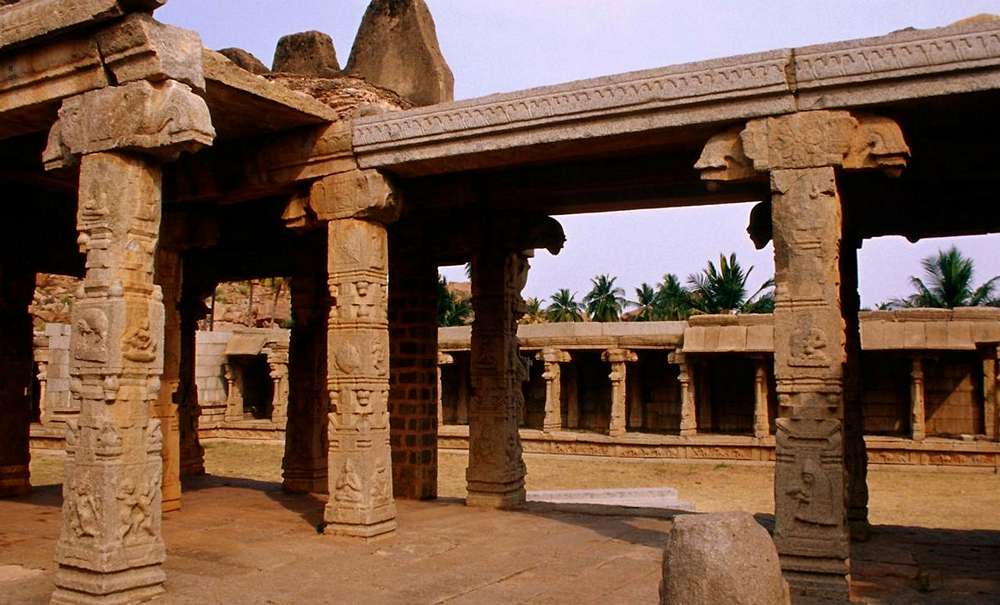
 On the pillars of the mukhamandapa are found passionate couples in various
On the pillars of the mukhamandapa are found passionate couples in various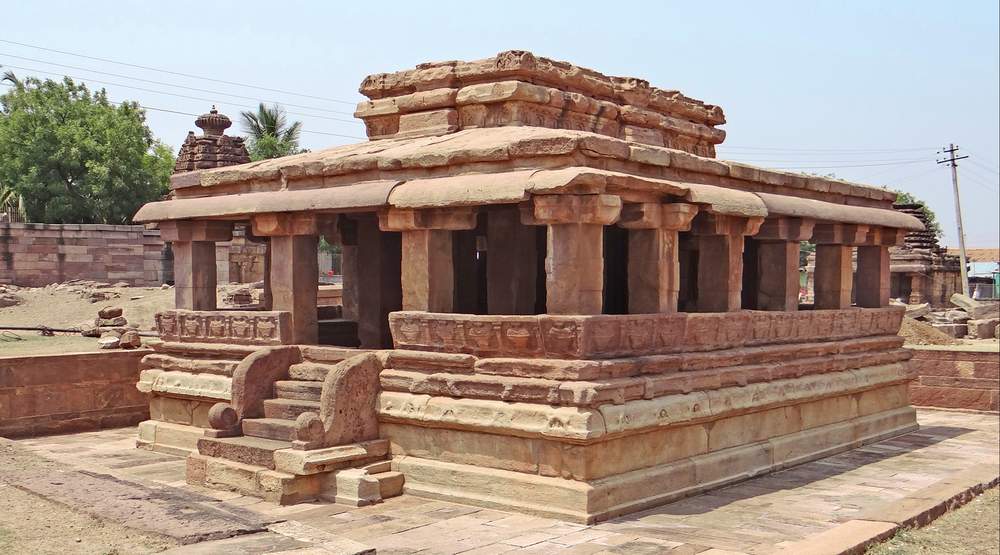 



 It has a distinctive plan and does not give the mark of a temple at all in the first instance. In reality, it looks like a
It has a distinctive plan and does not give the mark of a temple at all in the first instance. In reality, it looks like a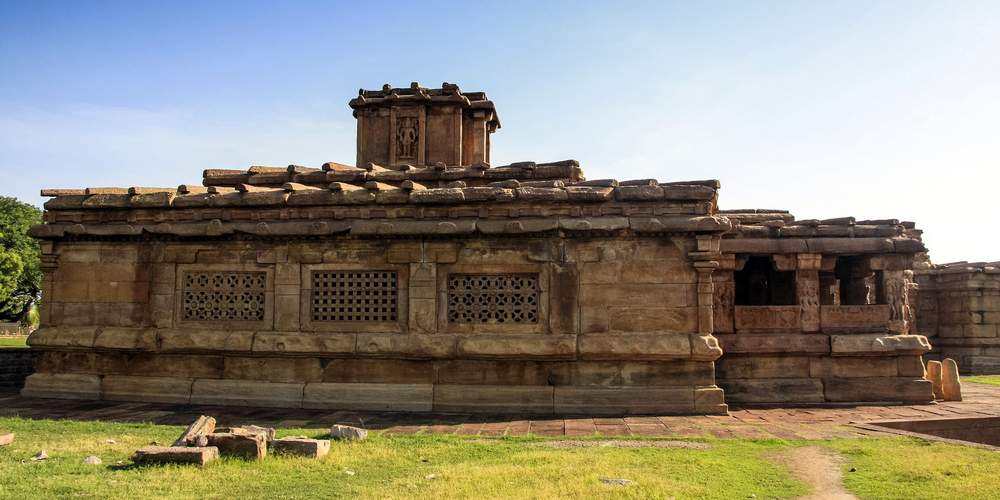 

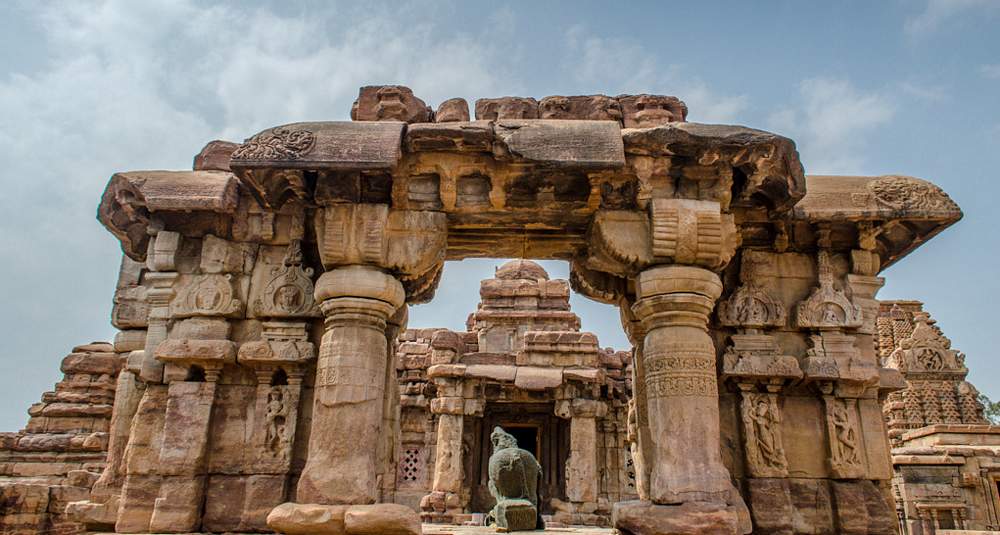
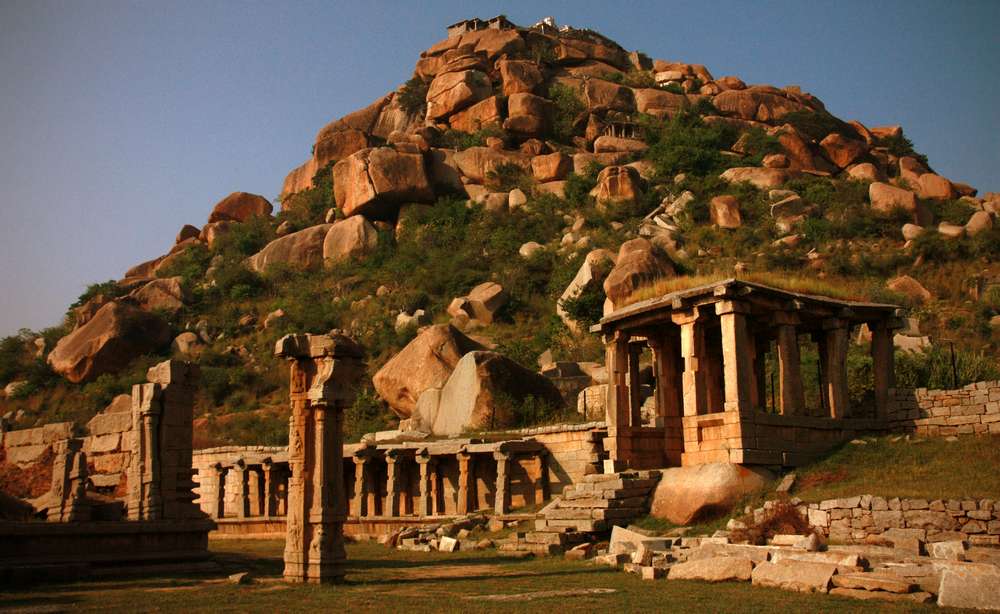
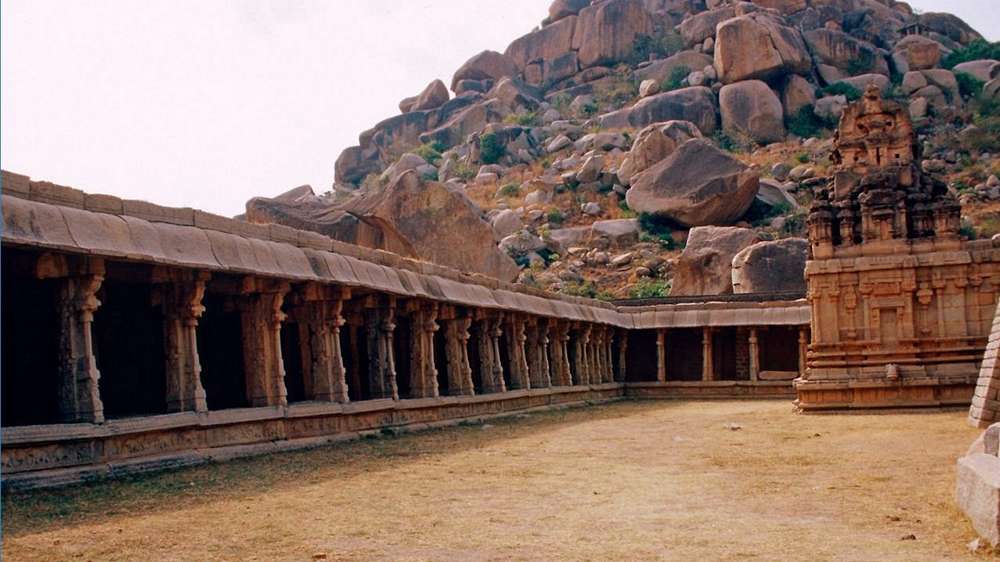
 The interior of the sanctuary is equally elegant and impressive. It consists of a large quadrangle, which measures 208 feet in length and 107 feet in width. This is divided into five aisles with the help of arches.
The interior of the sanctuary is equally elegant and impressive. It consists of a large quadrangle, which measures 208 feet in length and 107 feet in width. This is divided into five aisles with the help of arches.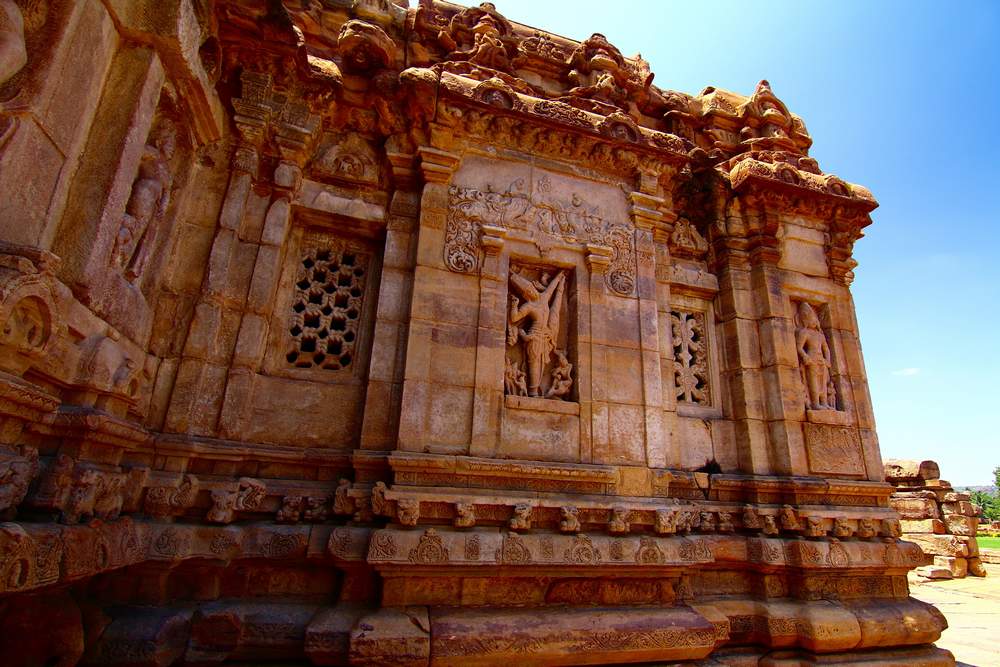



 Both
Both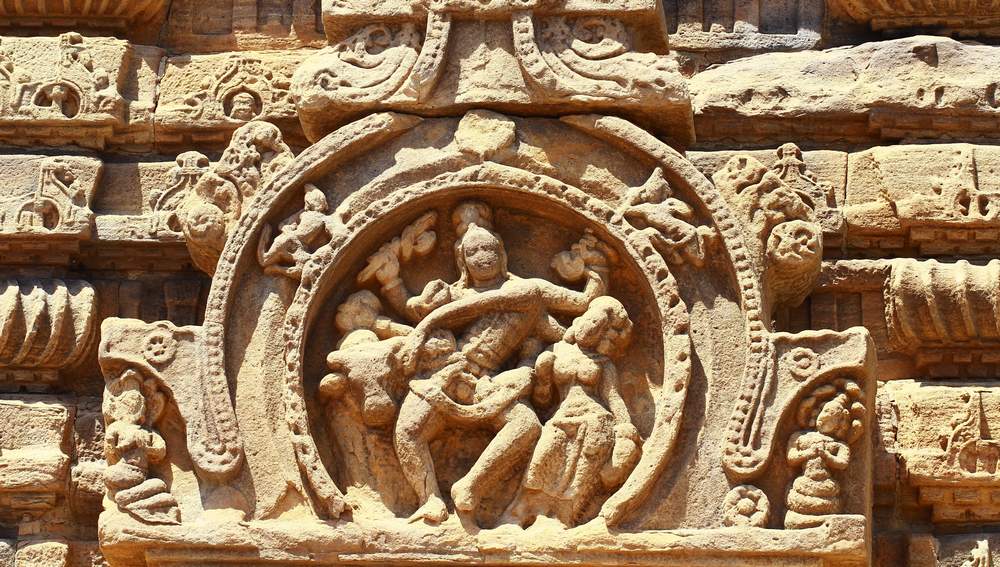 
 There were master architects like Revadi Ovajja, Anivarita Gunda, supported by sculptors like Changamma, Pullappan, Baladeva, et cetera. It also had the guidance of dance masters like Achalan and devadasis like Chalabbe. More than all, the
There were master architects like Revadi Ovajja, Anivarita Gunda, supported by sculptors like Changamma, Pullappan, Baladeva, et cetera. It also had the guidance of dance masters like Achalan and devadasis like Chalabbe. More than all, the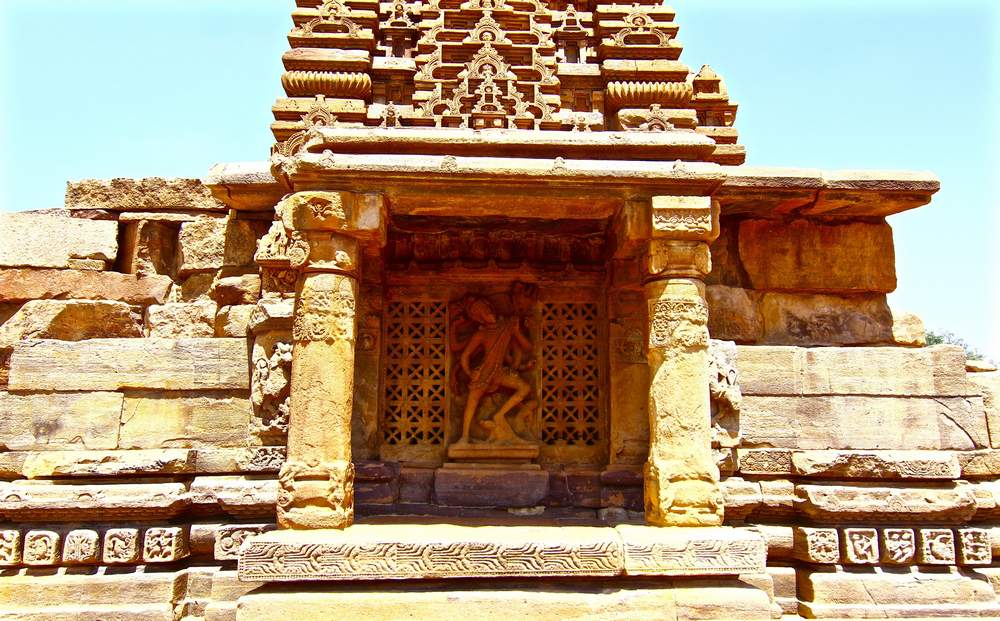 
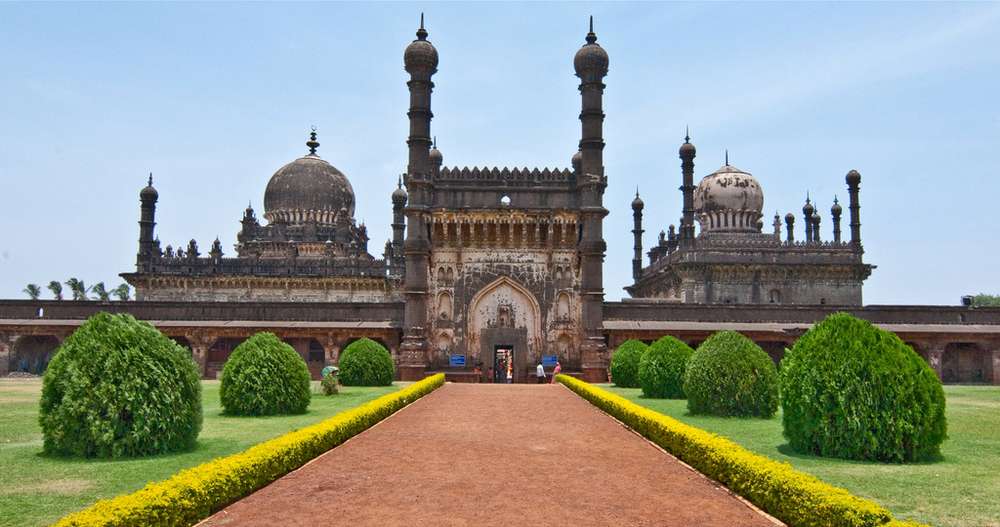

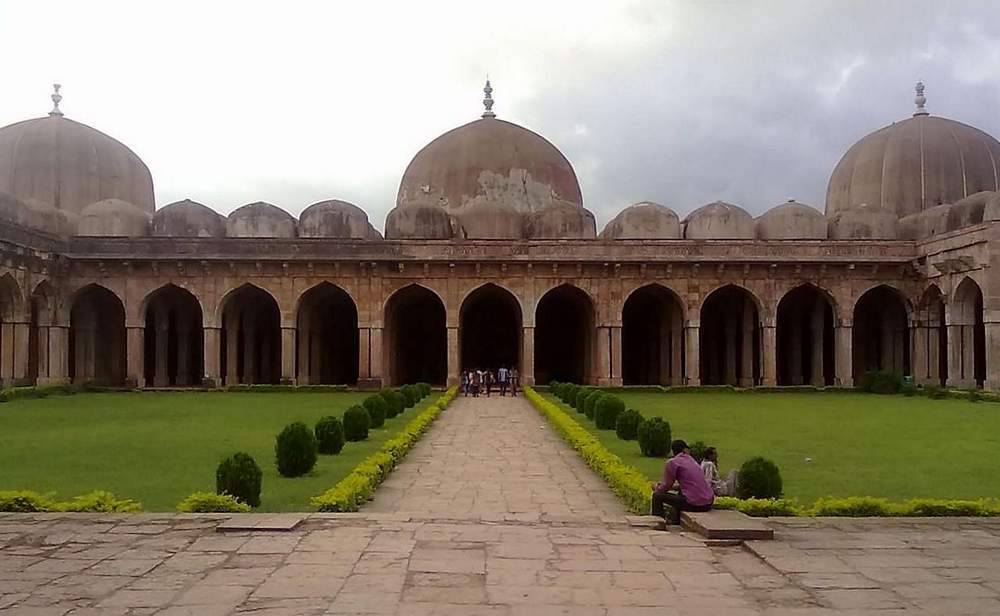
 Ibrahim Rauza consists of two core constructions: a tomb and a mosque with several smaller structures. All these buildings are built within a square enclosure with an attractive garden in the front. Both the structures are built on a platform that is 360 feet long and 160 feet wide, around a walled enclosure.
Ibrahim Rauza consists of two core constructions: a tomb and a mosque with several smaller structures. All these buildings are built within a square enclosure with an attractive garden in the front. Both the structures are built on a platform that is 360 feet long and 160 feet wide, around a walled enclosure.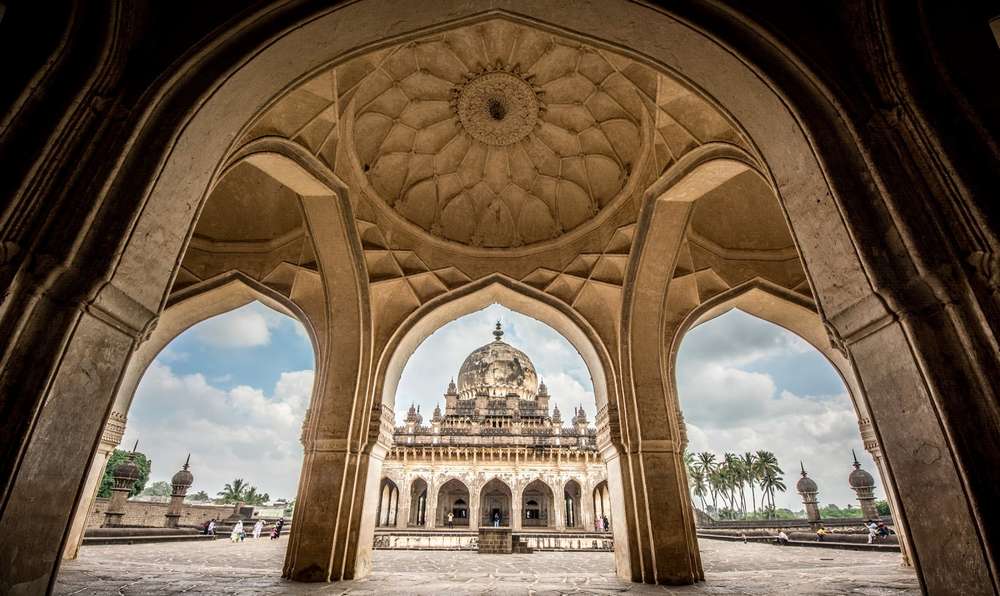
 The mosque forming the other part of the Ibrahim Rauza relates harmoniously in the mass of its proportion and architectural treatment as well as width of frontage. Though it seems slightly smaller, the comparisons overlook in terms of minars at four directions and a slightly smaller elongated dome. This congruence is the real uniqueness of the Ibrahim Rauza. Between the two and in the center is a beautiful entrance with two minars at each corners. Thus, the whole composition is highly appealing.
The mosque forming the other part of the Ibrahim Rauza relates harmoniously in the mass of its proportion and architectural treatment as well as width of frontage. Though it seems slightly smaller, the comparisons overlook in terms of minars at four directions and a slightly smaller elongated dome. This congruence is the real uniqueness of the Ibrahim Rauza. Between the two and in the center is a beautiful entrance with two minars at each corners. Thus, the whole composition is highly appealing.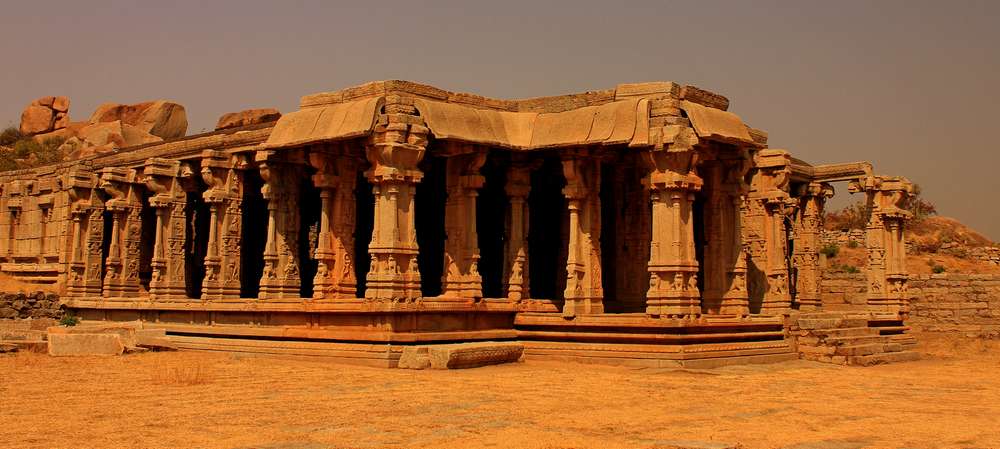
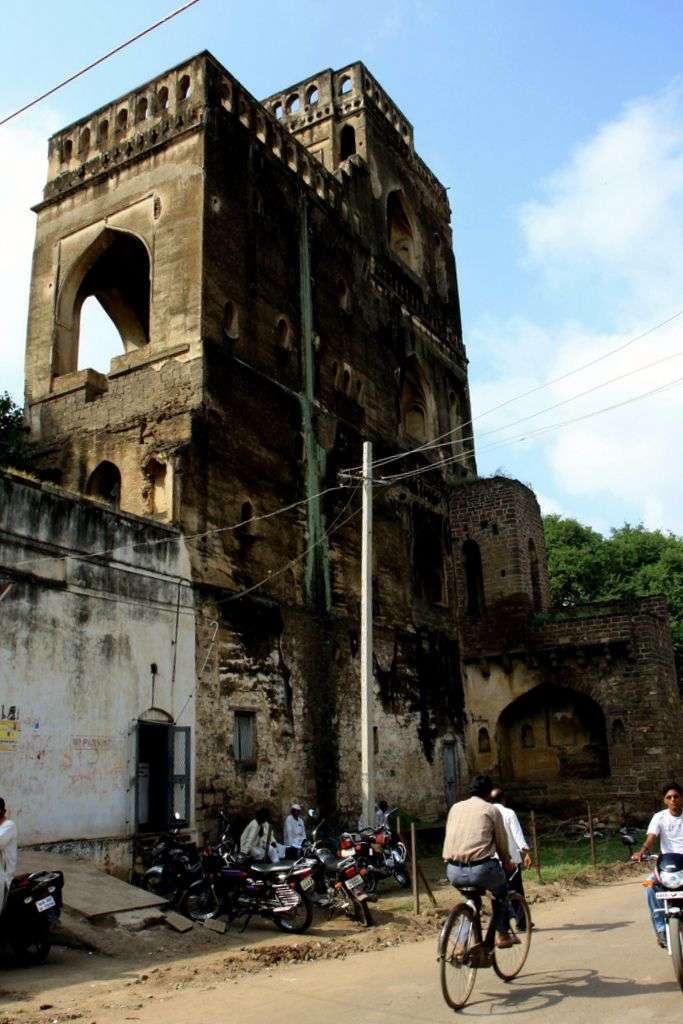
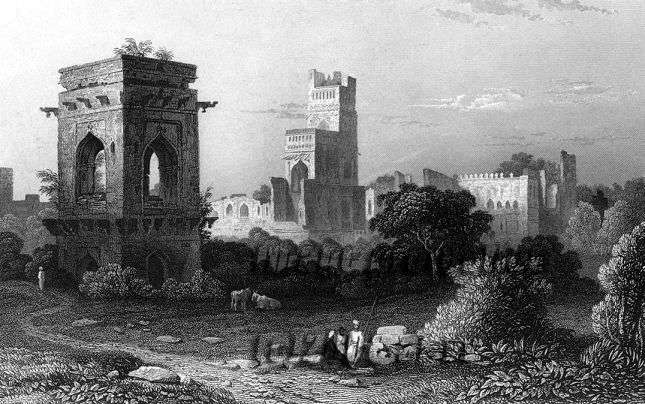










 Sath Manzil palace was far more extensive than it is today. Therefore, what we see today is only a partial palace and the remaining parts have been destroyed. The
Sath Manzil palace was far more extensive than it is today. Therefore, what we see today is only a partial palace and the remaining parts have been destroyed. The  Water cisterns are found on all the stories of this building. The walls of these bathrooms were painted with human figures and others decorative motifs. The walls were also gilded beautifully and luxuriously. Another noteworthy feature of this beautiful building is the extensive use of wood as in the case of pillars, window frames, window screens, and brackets. There is another building called
Water cisterns are found on all the stories of this building. The walls of these bathrooms were painted with human figures and others decorative motifs. The walls were also gilded beautifully and luxuriously. Another noteworthy feature of this beautiful building is the extensive use of wood as in the case of pillars, window frames, window screens, and brackets. There is another building called